Knits
Interweaving of a single thread forming loops passing successively through each other.
This technique of textile formation allows to obtain a flexible, comfortable, breathable and especially elastic material due to its particular structure.

Knit processing
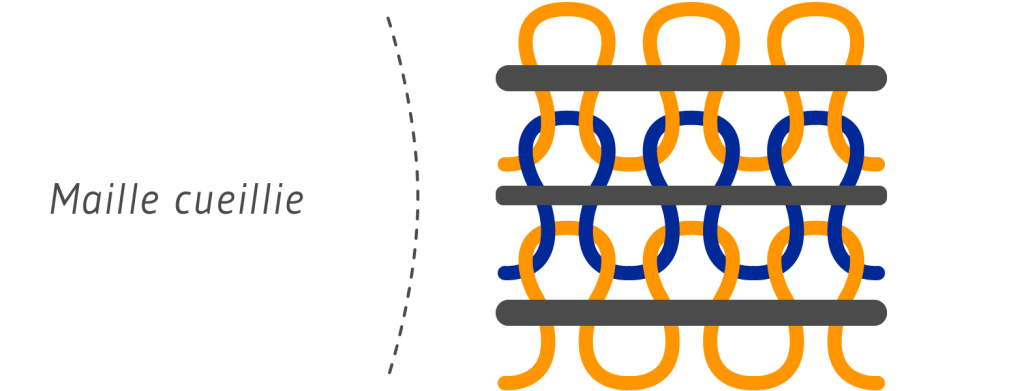
There are two distinct types of knitted fabrics, plucked and cast-off. Picked stitch is made up of a single yarn forming intertwined loops. Picked stitches can be formed on two types of knitting machines.
The circular loom
The knitted fabric is formed in a circular fashion, which allows a higher speed of output than the flat loom, but less freedom in the width of the color range present in the same knitted fabric.

The flatbed loom
Allows to form a flat knit. Depending on the machines used, it is possible to make complex structures, to use many different colors of yarns and semi-finished products called fully fashioned or finished called whole garment.
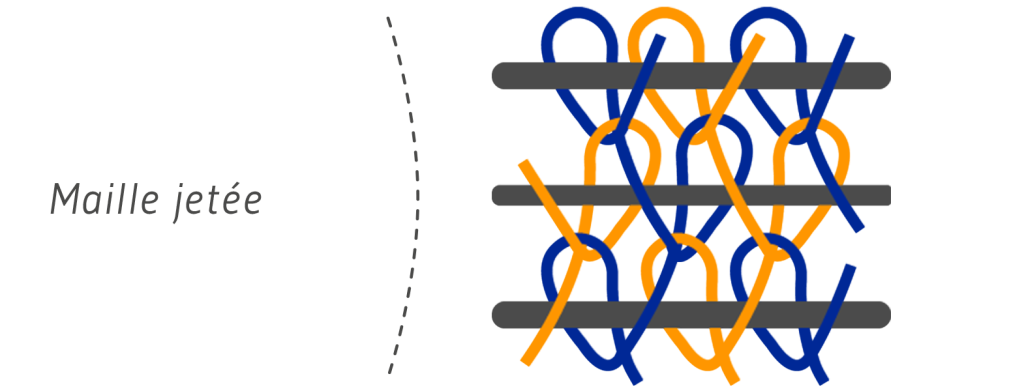
Wrap knitting
Is a particular knitting technique that allows to form a knitted fabric called “unknottable”. Each needle has its own thread, in case of breakage, each thread being independent, the surface will not unravel entirely. This stitch is formed on Rachel looms, straight or circular, mainly used to make tights and lace.
3D knitted fabrics
Used in fields such as aeronautics or automotive. They are either flat knitted fabrics formed in 3 dimensions, or spacer type knits, more or less thick. For this type of surface, synthetic materials are preferred.
The main knitting conjonctures
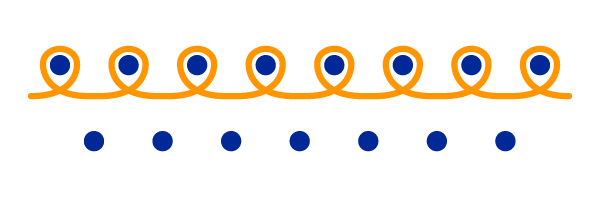
Jersey
The most widespread knitwear conjuncture, it is notably used for the manufacture of t-shirts and underwear (often made of cotton).
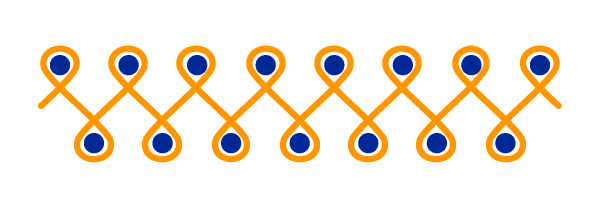
The 1-1 rib
A fairly widespread knitting technique, it provides more hold and thickness than stockinette by avoiding rolling.
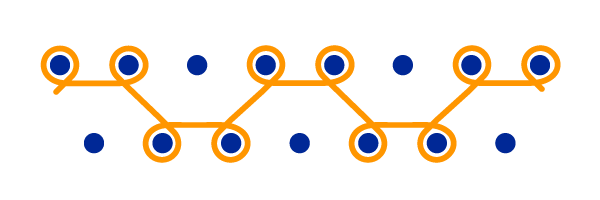
The 2-2 rib
Most often used for the manufacture of ribbed edges such as cuffs, collars or bottoms of clothing.
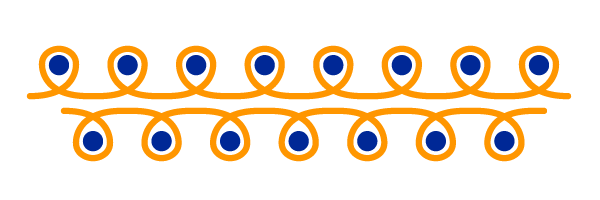
The tubular
This conjuncture makes it possible to carry out a circular stitch on a rectilinear loom. It alternates a front stocking followed by a back stocking.
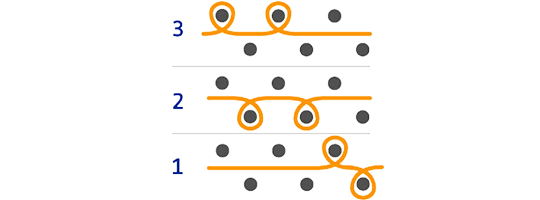
Iinterlock
Complementary stitches that allow to obtain a knit with a higher density, therefore denser and more rigid
Types of materials processed
Knitting processes most soft materials. Natural plant fibers are mostly too thick and stiff to knit. Knitting is mainly for wools, cotton and organic chemical materials.
Characteristics
Knitwear provides a soft, elastic and comfortable material (if compared with fabric).
Picked mesh is deformable, has low mechanical strength, is easy and quick to set up but is fragile and easily unraveled.
Thrown mesh is also elastic and flexible, but it is more resistant and is said to be unbreakable. It is more complicated to implement.
Applications
Apparel, sports, filtration, insulation, industry, safety / PPE, furniture, household lienen, medical, etc.


