Fabrics
Interweaving of threads of which a part is in the vertical direction (called warp direction) and the other part in the horizontal direction (called weft direction).
The fabrics are obtained by weaving on manual or automatic looms. The threads in the warp direction are alternately raised or lowered according to the desired pattern. Between each movement, a thread in the weft direction is inserted and then compacted, using a comb, to form the fabric.

Fabrics processing
There are three main families of weaves, each has many variations.
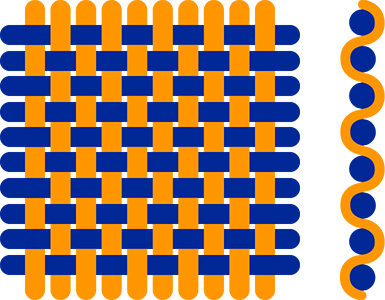
Canvas
This is the most classic and widespread weave.
It alternates a taken warp thread and a left one, then reverses on the next line. This weave allows to have a solid, resistant, relatively thin and homogeneous fabric. It is often used in technical textiles for its strength and ease of implementation.
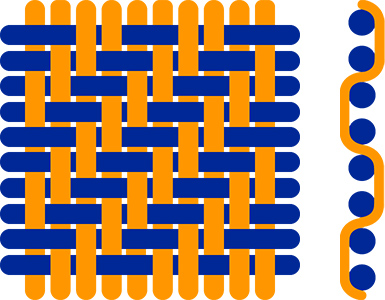
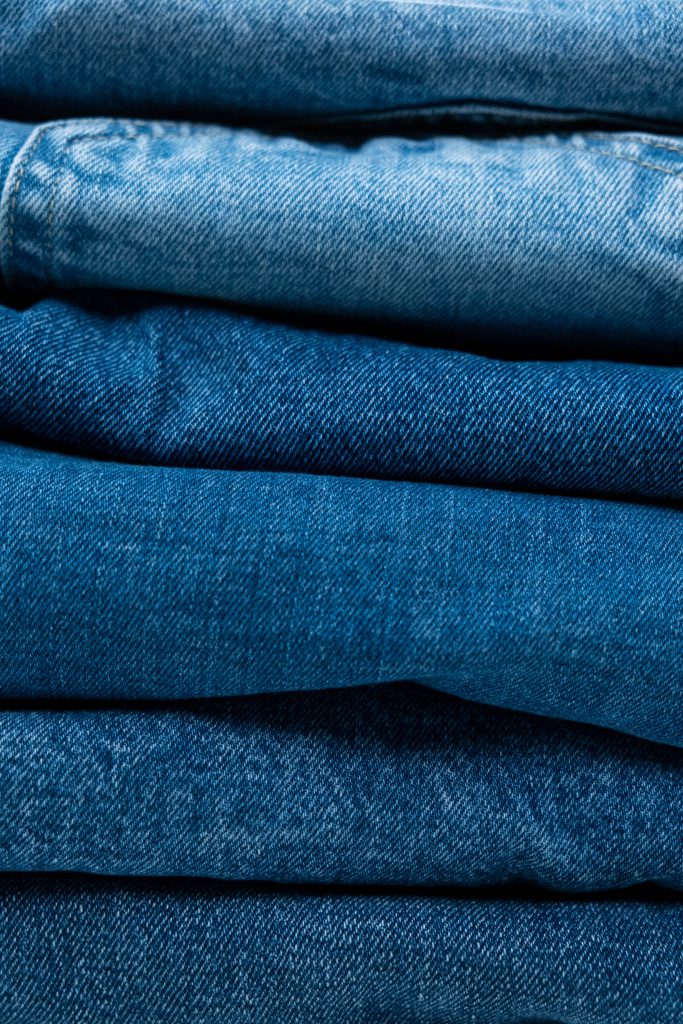
Twill
This weave allows the formation of cords (line effect) formed in diagonals.
It also allows to obtain a resistant material. It is mainly used in the manufacture of jeans and work clothes.
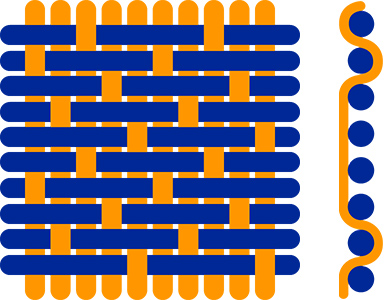
Satin
This weave has the particularity to have few taken yarns, which leaves important lengths of left, so, we see appearing floats.
This weave is mainly used in clothing for its very shiny and soft effect, as in the case of silk, but also in technical textiles for anti-cutting applications.
Other weaving methods

Jacquard
Is set up on looms called jacquard, they have the particularity of having independent threads of chains. This type of loom allows total freedom in terms of patterns. Nevertheless, the number of colors is limited and depends on the machines.
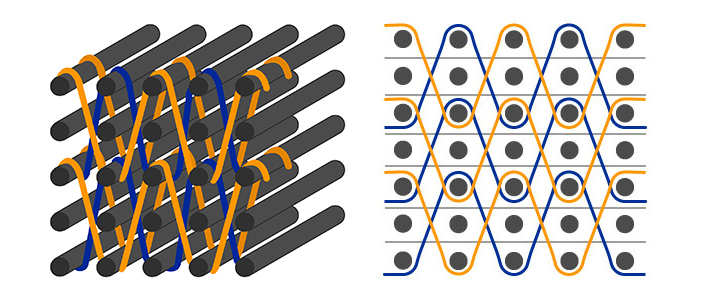
Interlock
Mainly in technical textiles, we also find 3D interlock woven structures, this weaving technique allows to obtain multi-layer fabrics. They are particularly effective in resisting high speed projectiles (e.g. explosive devices), they allow to distribute and absorb the shock caused by the impact.
Types of fibers used
Weaving can use all types of yarns, from all origins. It is easier to weave natural fibers because they are less smooth and therefore slip less.
Characteristics
Resistant, dimensionally stable, durable. The characteristics depend on the weave chosen.
Applications
Clothing, geotextiles, composites, parachute fabrics (paragliders etc.), boat sails, safety / PPE (personal protective equipment), health, food packaging, furniture, sports equipment, events, industry, etc.


