Printing and fabric details
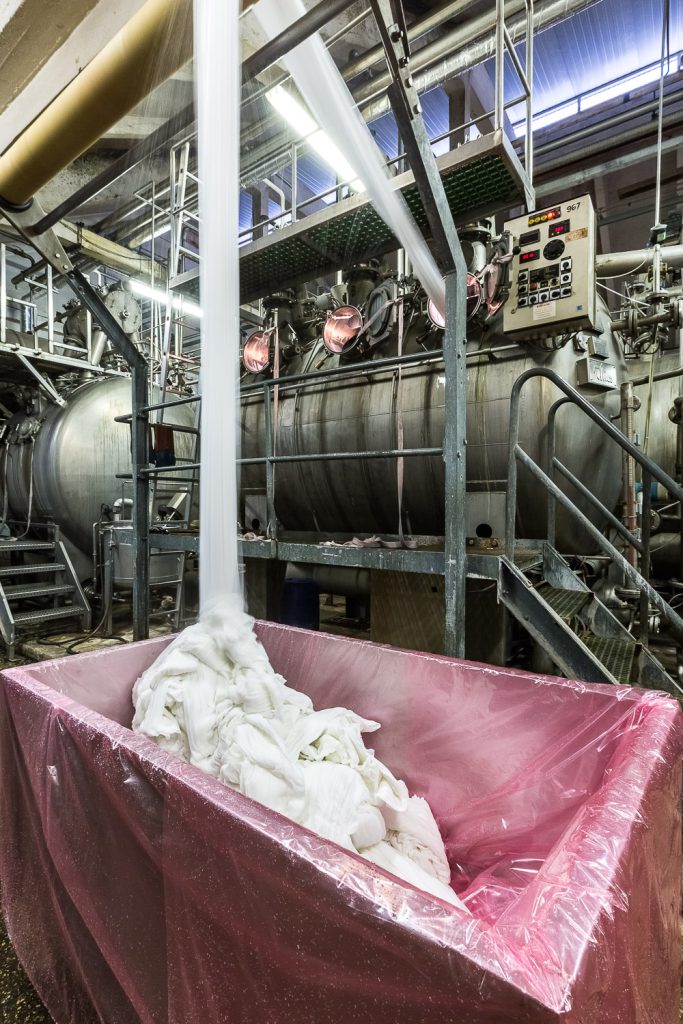
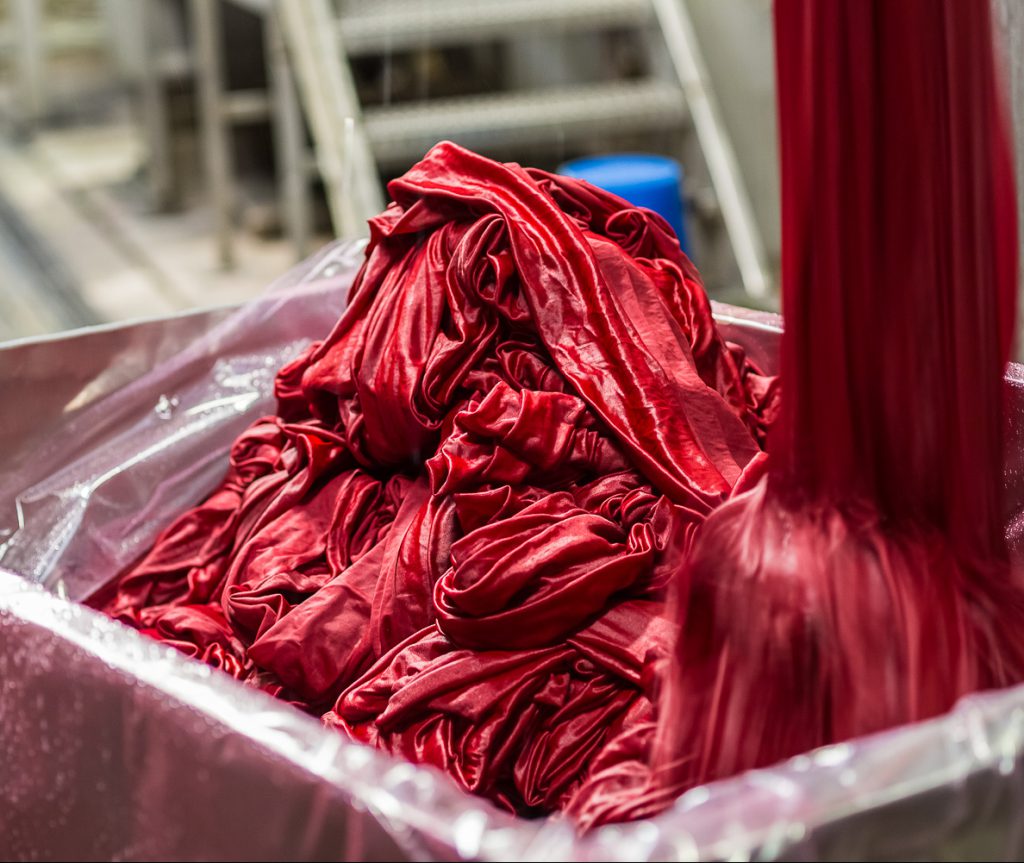
Textile printing is a localized coloring, it is carried out on the textile or directly on the finished part.
For most textile printing, pigments are used instead of dyes. The difference is in the size, a pigment is much larger, so it will not nestle in the heart of the fiber, but remains on the surface.
For a successful printing, it is necessary to prepare the material well to avoid staining.
The textile details allow to bring functional or decorative elements to the textile pieces.

Printing or fabric details types
Flocking
Consist in printing a pattern on a flex roll then sticking it on the textile thanks to a hot press. This technique is the most widespread. It is applicable only in the case of a simple pattern, little colored but compatible with all compositions and with a correct lifespan.
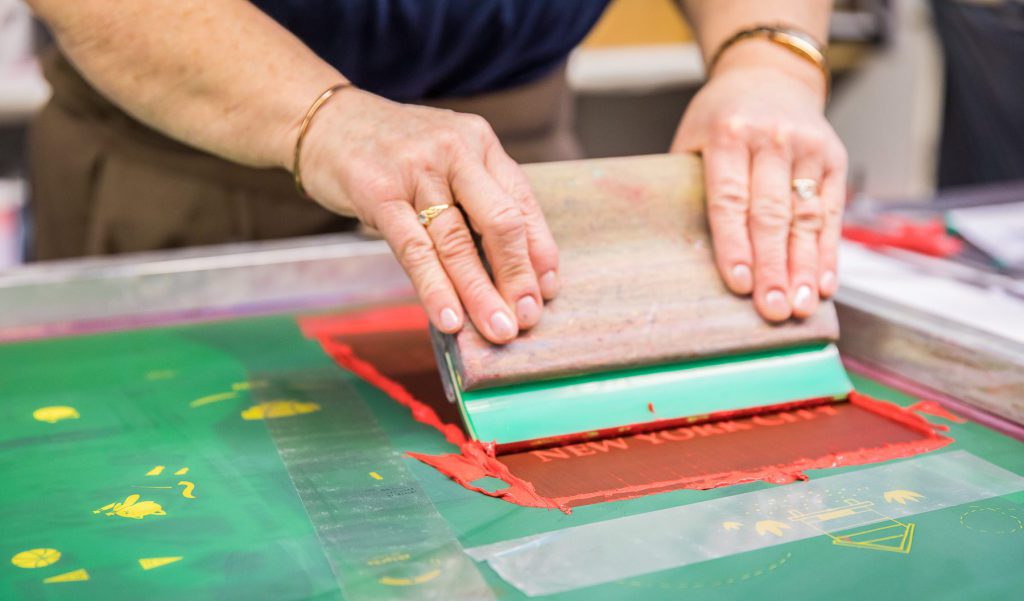

Silk-screen printing or rotary printing screen
The oldest printing process. A screen is equipped with a tended fabric perforated according to a motif, as a stencil. The screen is then laid out on the textile, one deposits a pigmented paste which one comes to scrape on the fabric.. This operation must be repeated as many times as there are colors on the desired pattern (one screen per color). This technique is intended only for medium or large series.
For the printing of a textile with the continuous one, in the same principle as the serigraphic impression for the textile decoration, one uses a rotary printing screen. The pattern is perforated on a cylinder of the width of the textile, one comes then to deposit the paste of impression inside the cylinder. A scraper allows to homogenize the layer of paste deposited.
It is necessary to use a different rotary screen by color, this process is intended for large series and treats the reasons having few colors.
Inkjet / Digital printing
Principle similar to paper printing, It allows to print small patterns but also textiles in rolls (mesh or fabric) for materials composed mainly of cotton. It allows a great freedom at the level of the colors. This process does not consume water and little energy. This technique allows a strong wash fastness.
Transfer printing
Technique which consists in printing a pattern or an image on a transfer paper, via a digital printer. It will then be applied on the textile product by the contact of a hot press for finished articles, and a heating drum to print textile in a continuous way.
Transfer printing is also used to add adhesion by dots to some products (socks or riding pants for example).It is a very widespread process, especially in customization on demand or little series. This technique is not very time resistant and inexpensive.
Sublimation
Technique which consists in printing the motif or the personalized pieces of textile on special paper. The ink will, under the heat action of a hop press or a calender, gasify and penetrate directly in the heart of the fiber. This technique allows a very strong wash fastness. This technique is used extensively in the field of sports, but can only be applied to organic synthetic materials in white colors.
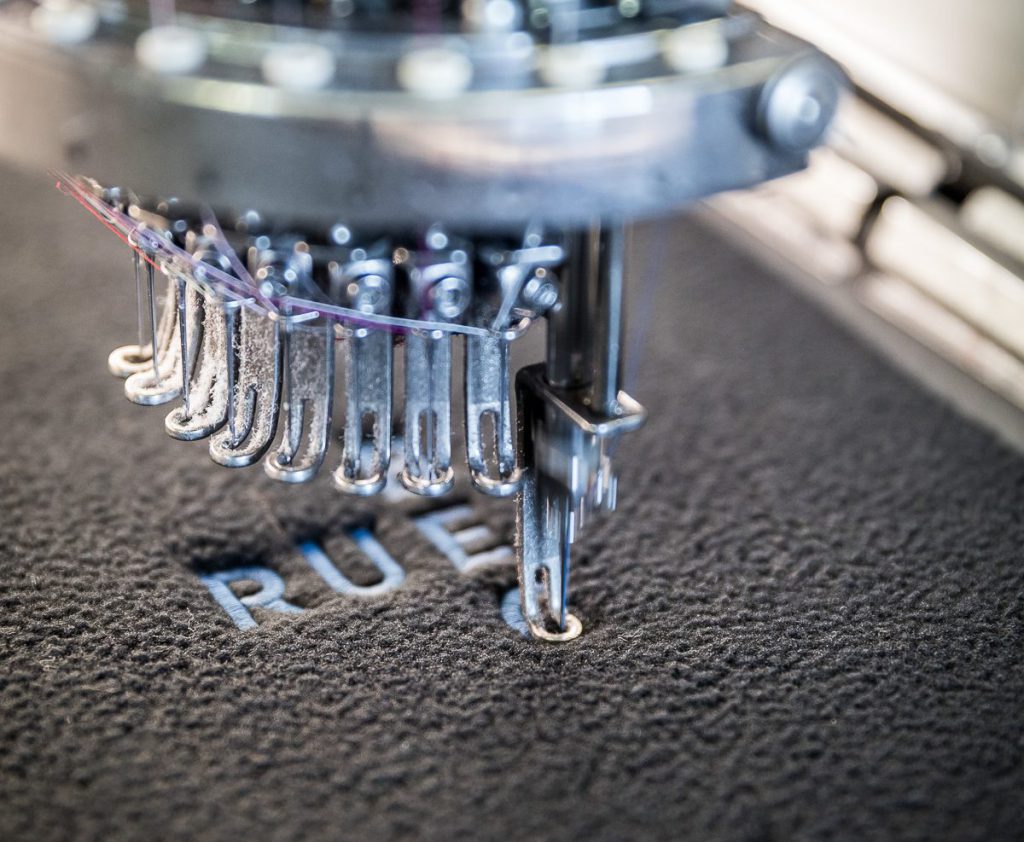
Embroidery
Creating a pattern or shape by accumulating the passage of threads. Often used for aesthetic purposes, embroidery can also allow a transfer of information or electricity via a conductive yarn.
3D printing
Allow the deposit of viscous materials by nozzles. This technique can be used to create shapes or volumes on textile surfaces, but also, like embroidery, can depposit a yarn to bring conduction to the garment.





