Composites
Intimate assembly of several immiscible materials (which do not mix), of different nature and whose qualities complement each other with synergy in order to obtain a heterogeneous material.
Composed of a matrix and a fiber reinforcement (textile), whose performances are superior to those of its components.
- The reinforcement allows to resist to the mechanical solicitations.
- The matrix (resins or thermofusible materials) allows to maintain the reinforcement, to bring a shape, to protect the reinforcement, to transmit and distribute the mechanical solicitations to the reinforcement.

Composites processing
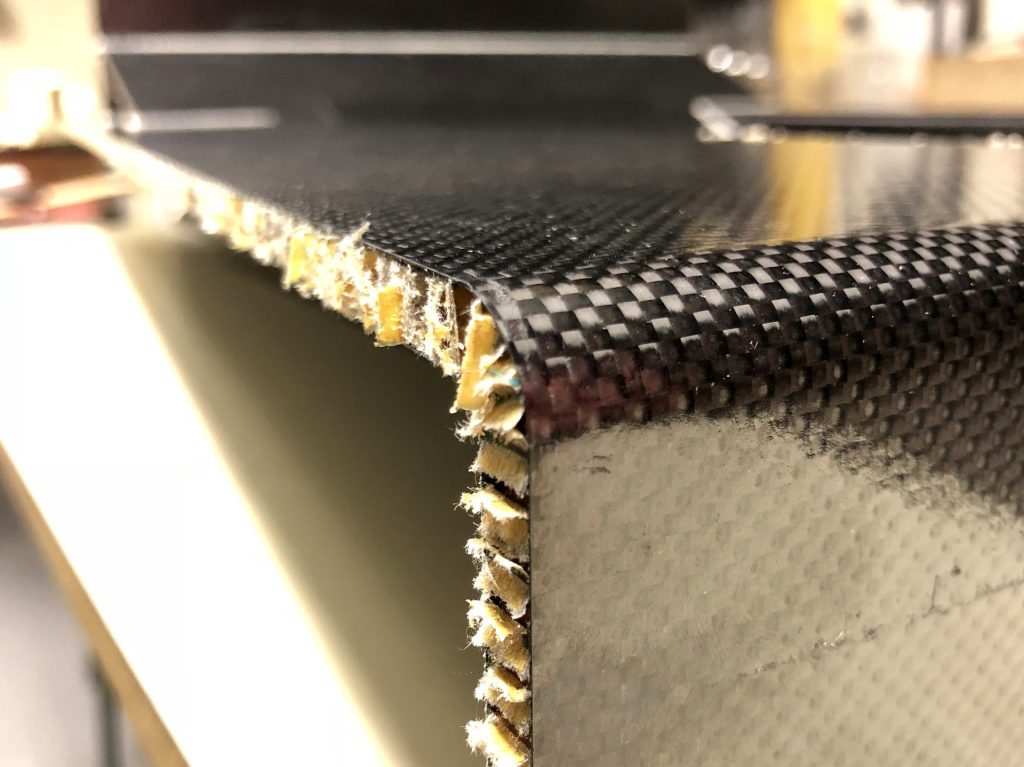
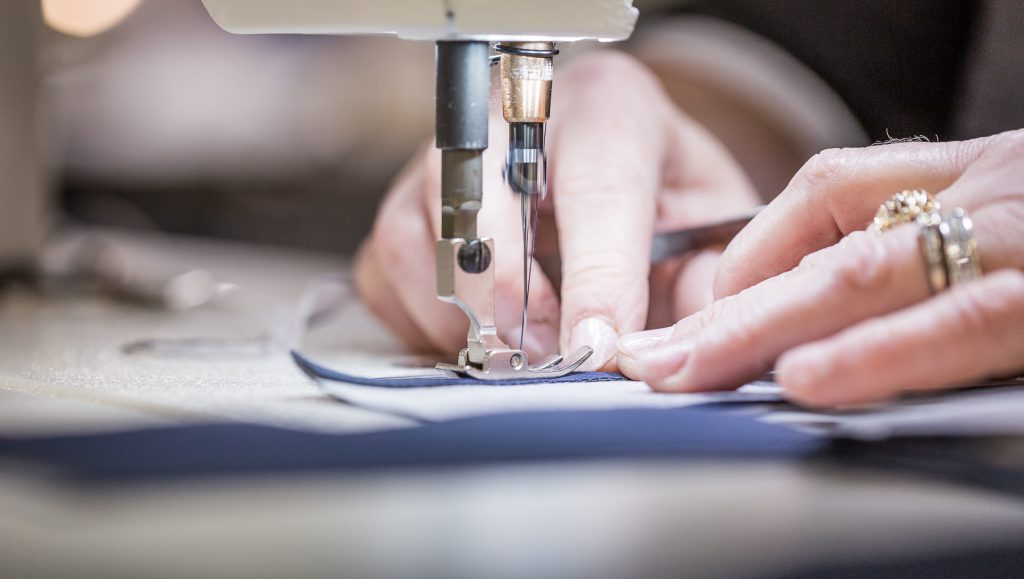
Composites processing
It is necessary to prepare the reinforcement, knit, fabric, nonwoven or other. The matrix can be applied by several methods.
First, directly in the material, if we have a textile made of two materials, one thermofusible and the other not, it is enough to heat the surface to the desired shape.
If the matrix is added separately, impregnation, infusion, splashing, prepreg, compression molding or a centrifugation can be performed.
Types of materials processed
Mainly inorganic synthetic materials (carbon, glass) and blends of natural fibers (such as linen or hemp) with thermofusible fibers such as polypropylene.
Characteristics
Solid and rigid while remaining light, weariness of use, corrosion proof, complex geometry possible.
Weaknesses : anisotropic (not homogeneous), expensive, long and costly implementation.
Applications
Automotive, nautical, aeronautics, energy, sport equipment, etc.





